Physical Link : transmitter -> Receiver
Guided media : signals propagate in solid.
copper(Ethernet), fiber(HFC) , coax
Unguided media : signals propagate freely.
no physical "wire", radio link type ex) WIFI, Cellular(wide-area), terrestrial microwave, satellite
End systems --> access networks --> links --> access network--> End systerms
1.3 Netwrok core : packet switiching, circuit switching, network struture.
Host Role : sends packets of data
- takes application messgage
- break into smaller chunks, known as packets, of length called L bits
- transmits packet into access network at transmission rate R
= packet size(bits) = L / link transmission rate(bits per sec) = R (L/R)
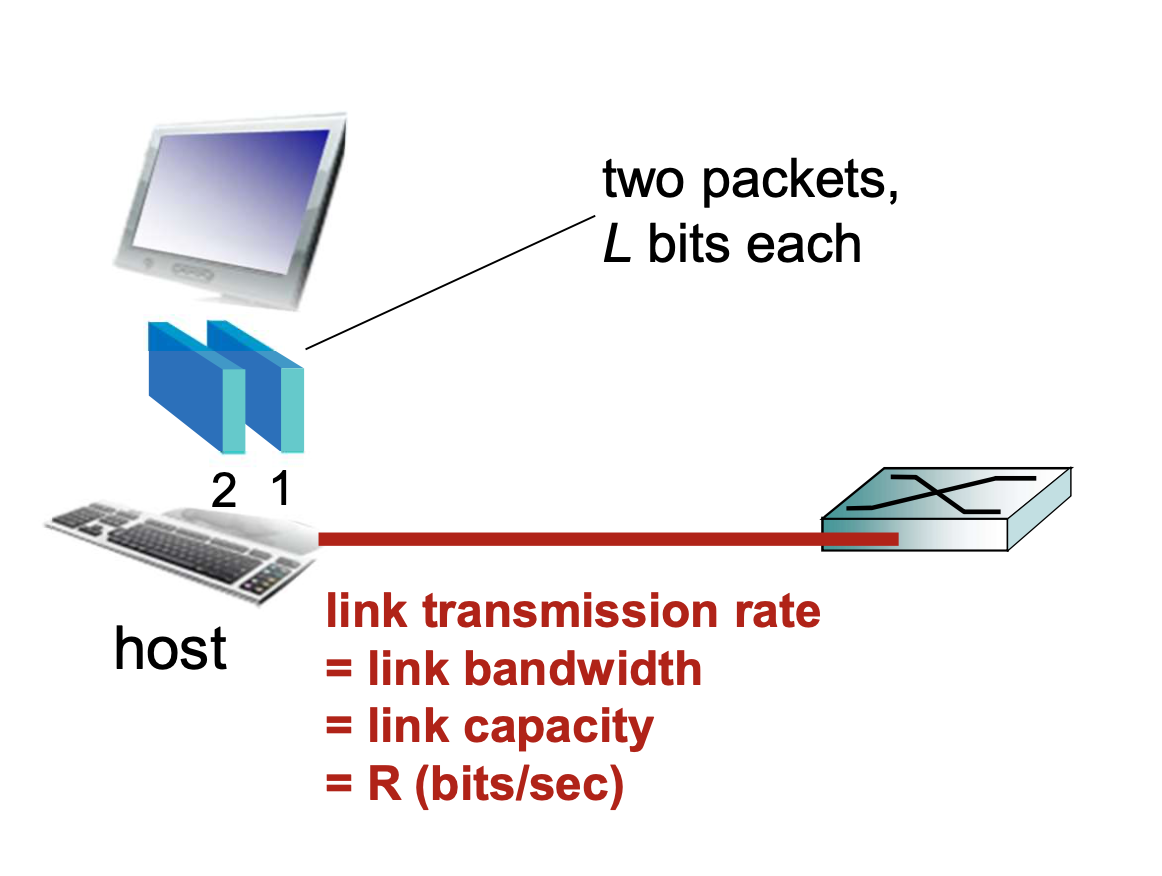
Why breaking down a packet?
1. Core network delivery efficiency : 패킷 손실 시 손실 된 부분만 다시 보내면 되어서(retransimission).
2. Shared media multiplexsing : Access network는 보톧 shared, 어느 한 user가 잡고 있지 않도록 하기 위해서(여러 user의 패킷을 고르게 전송).
3. Parallel : 작은 사이즈의 packet으로 쪼개 보내면 end to end delay 감소.
Packet Switching : Internet networks
- no call set up & no resource reserved
- packet transmitted at full link capacity
- packet-switching : host break application-layer messages into packet.
In the packet there is destination addpress.
a Routher have to store up the full packet before pasing for figure out the packet's destination address than it can transmitted on next link(routher).
1. Store : store a data up
2. Forawrd : pasing for data destination
Queueing delay : congestion

If arrival rate( in bites) to link exceeds transmission rate of link for a period time:
- packet will queue, wait toe be transmitted on link.
- packets can be dropped(lost) if memory(buffer) fills up.
Internet structure : network of networks
Communication link issues
Effective distance : 제대로 성능을 발휘할 수 있는 거리(Link type이 결정)
Bandwidth : 어느 정도 용량의 data traffic까지 수용 가능하지(bps)
error ratio : erro가 없어야 함
Core Network : Postal service(Delivery)
Core network의 핵심은 지구 상의 누구와도 통신할 수 있도록 core network를 구성하는 router들이 meshed 상태어야 함
가장 핵식점인 기술 : packet/circuit switching
Mesh of interconnected routers(Meshed network : 임의의 두개를 골랐을 때 어떻게든 연결이 되어 있어야 함)
Packet switching
Host breaks an application-layer messages down into a packet.
(Datagram) Packet Switch Functions

Routing : packet의 헤더값을 보고 Routing table만듦.
Forwarding : Packet을 다음 router의 Output port로 전송(=switching)
Local Level 개념으로써, Routing을 통해 다음 Router를 이미 알고 이에 기반하여 Forwarding input port로 들어온 패킷을 어떤 output port로 내보내는 것 -> store-and-forward
store-and-forward
왜 Store를 하는지? 헤더를 시작으로 한 Packet 단위로 전송되기 때문에 하나의 packet이 모두 들어올 때까지 기다림.
L-bit packet을 R bps 링크에서 비트에서 시그널로 전환하는데에 L/R sec가 걸림
Router의 Input 버퍼에서 L bits 다 올때까지 store-and-forward가 일어남
순서 정리
L개의 비트들이 A 포트의 buffer에 저장된다.
패킷해더를 보고 목적지 주소를 보내기 위해 라우팅 테이블을 검색한다.
L-비트 패깃이 A에서 B로 스위칭 된다.
L-비트 패킷이 B의 buffer (queue)에 한동안 저장되어있다.
L개의 bit들이 signal로 변환(transmit) 된다.
Circuit switching : telephone networks
- cell set up & resource reserved(packet 자체가 필요 없음)
--> Find a Route and which line is going to be set up all(Delay zero)
--> No sharing and all bandwidth occupied
FDM : allocated Frequency(주파수 할당)
TDM : allocated Time(시간 할당)

CPN(Content Provider Network) e.g Google
컨텐츠 제공 회사들이 직접 네트워크 장비를 증설.
전세계 어디에도 자기네 센터가 있으니까 Tier 1 ISP에게 돈을 주는 것보다 차라리 자기네꺼 장비증설이 더 저렴하니까.
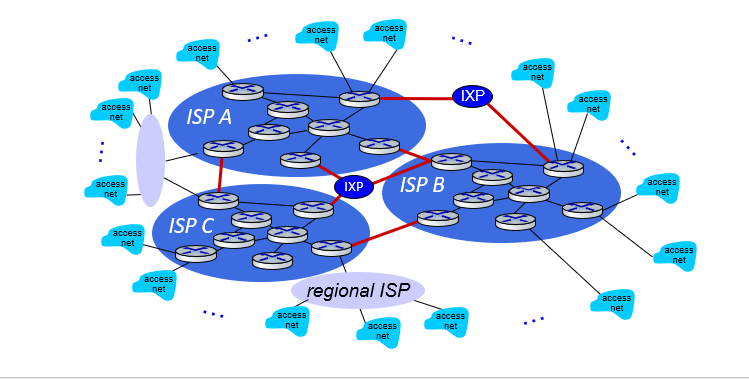
IXP : internet exchange point
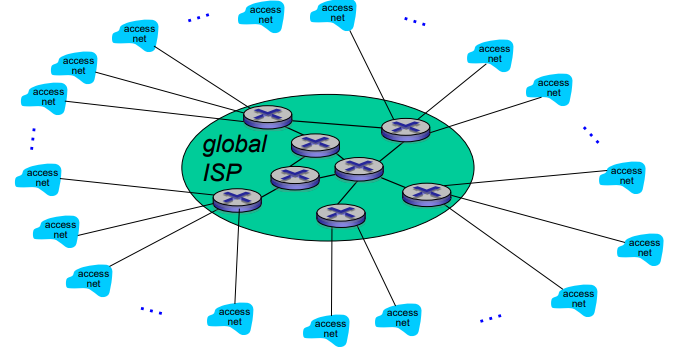
Core : network of networks
Regional ISP Multi-tier hierachy
First RISP(Only International connection ISP Lv) > XL RISP > L RISP > M RISP > S RISP > XS RISP
출처
이화여대 컴퓨터 네트워크 (2014년)
https://velog.io/@lychee/%EB%84%A4%ED%8A%B8%EC%9B%8C%ED%81%AC-1-2.-Access-network-Core-network
'UI > Dev_Knowledge' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Lecture] 4강 / Chapter2 : Layers (0) | 2023.08.23 |
|---|---|
| [Lecture]Network 3강 : 1.4 delay, loss, throughput in networks (0) | 2023.08.19 |
| [Lecture]Network 1강 (0) | 2023.08.14 |
| [Front-End]HTML에서 토큰화와 어휘분석? (0) | 2023.07.22 |
| [Front-End] 브라우저 엔진과 렌더링 엔진의 차이는 뭘까? (0) | 2023.07.22 |



